Raw chemicals are routinely used worldwide. From initial production through final disposal, many of these chemicals pose a threat to humans and to the environment. Historically, most countries have implemented some form or another of regulating chemical hazards. This has resulted in numerous standards with many discrepancies. For instance, one country might designate a chemical as toxic while another country might consider that same substance nontoxic. Different classification systems can even be found within the same country. Add differing languages and alphabets to the mix and it’s clear that the time has come to establish a global standard.
What is GHS?
GHS is an acronym for the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals, a framework that standardizes the classification and labeling of chemicals worldwide. Its goal is to establish criteria for the classification of health, physical and environmental hazards, and specify what information should be included on hazard labels as well as safety data sheets. As a global standard, GHS encourages individual countries to implement hazard classes and categories in their legislation.
The United Nations adopted GHS following the 1992 UN Conference on the Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The International Labour Organization (ILO), The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), and governments from all over the world cooperated to create and promote a universal standard to classify of health, physical, and environmental hazards.
GHS Implementation Timeline (United States)
| Date | Requirement | Applies to |
|---|---|---|
| December 1st, 2013 | Train all employees on the new label elements and Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Format | Employers |
| June 1st, 2015 | Chemical manufacturers, importers, and employers must comply with all modified provisions of this rule (distributors that are allowed to ship products labeled by manufacturers under the old system up until Dec. 1, 2015) | Chemical manufacturers, importers, and employers |
| December 1st, 2015 | Distributors must comply with all modified provisions of this final rule. | Chemical distributors |
| June 1st, 2016 | Update alternative workplace labeling and hazard communication program as necessary, and provide additional employee training for newly identified physical or health hazards | Employers |
GHS Enforcement Guidelines (United States)
On February 9, 2015 the United States Department of Labor issued a memo titled Enforcement Guidance for the Hazard Communication Standard’s (HCS) June 1, 2015 Effective Date. The memo details the Department of Labor’s enforcement position and how the June 1, 2015 effective date will impact manufacturers, distributors, and employers.
Guidelines and clarifications include the following:
Manufacturers that have made reasonable and good faith efforts to meet the June 1, 2015 effective date, but have not been able to comply due to circumstances outside of their control, will be allowed a reasonable time period to come into compliance.
Following the December 1, 2015 distributors deadline, distributors can not ship using the old (HCS 1994-compliant) labels unless the distributor’s supplier falls into the above category, i.e., suppliers that have made reasonable and good faith efforts to meet the June 1, 2015 effective date, but have not been able to comply due to circumstances outside of their control.
Employers that have not received updated SDSs or labels for some of the hazardous chemicals they use in their business will not be cited by OSHA. However, Once they receive the new (HCS 2012-compliant) SDSs, they must maintain them.
GHS Pictograms and Hazard Classes
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals utilizes two sets of pictograms. One for workplace hazards, and a second for the transportation of dangerous goods.
Physical Hazards Pictograms:
| GHS Hazard | Pictogram | Hazard Class & Hazard Category |
|---|---|---|
| Explosive |  |
|
| Flammable |  |
|
| Oxidizing |  |
|
| Compressed Gas |  |
|
| Corrosive | 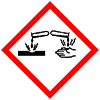 |
|
Health hazards pictograms:
| GHS Hazard | Pictogram | Hazard Class & Hazard Category |
|---|---|---|
| Toxic |  |
|
| Corrosive |  |
|
| Irritant |  |
|
| Health Hazard |  |
|
Environmental Hazards Pictograms:
| GHS Hazard | Pictogram | Hazard Class & Hazard Category |
|---|---|---|
| Environ- mentally Damaging |
 |
|
Transport Pictograms
Class 1: Explosives
| GHS Hazard | Pictogram | Hazard Class & Hazard Category |
|---|---|---|
| Divisions 1.1–1.3 |  |
Explosives
|
| Division 1.4 |  |
Explosives
|
| Division 1.5 |  |
Explosives
|
| Division 1.6 |  |
Explosives
|
Class 2: Gases
| GHS Hazard | Pictogram | Hazard Class & Hazard Category |
|---|---|---|
| Division 2.1 |  |
Flammable Gases
|
| Division 2.2 | 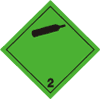 |
Non-flammable Non-toxic Gases
|
| Division 2.3 |  |
Toxic Gases
|
Classes 3 and 4: Flammable Liquids and Solids
| GHS Hazard | Pictogram | Hazard Class & Hazard Category |
|---|---|---|
| Class 3 |  |
Flammable Liquids
|
| Division 4.1 |  |
Flammable Solids, Self-reactive Substances and Solid Desensitized Explosives
|
| Division 4.2 |  |
Substances Liable to Spontaneous Combustion
|
| Division 4.3 |  |
Substances Which in Contact with Water Emit Flammable Gases
|
Other GHS Transport Classes
| GHS Hazard | Pictogram | Hazard Class & Hazard Category |
|---|---|---|
| Division 5.1 |  |
Oxidizing substances
|
| Division 5.2 |  |
Organic Peroxides
|
| Division 6.1 | 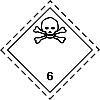 |
Toxic Substances
|
| Class 8 |  |
Corrosive Substances
|
GHS Labeling
As of June 1, 2015, GHS labels require pictograms, signal words, hazard and precautionary statements, product identifiers, and supplier identifications. The label can also include supplemental information as needed.


